Case Studies
Variable Rate Seeding Using Plant Available Water Layer Pt. 2
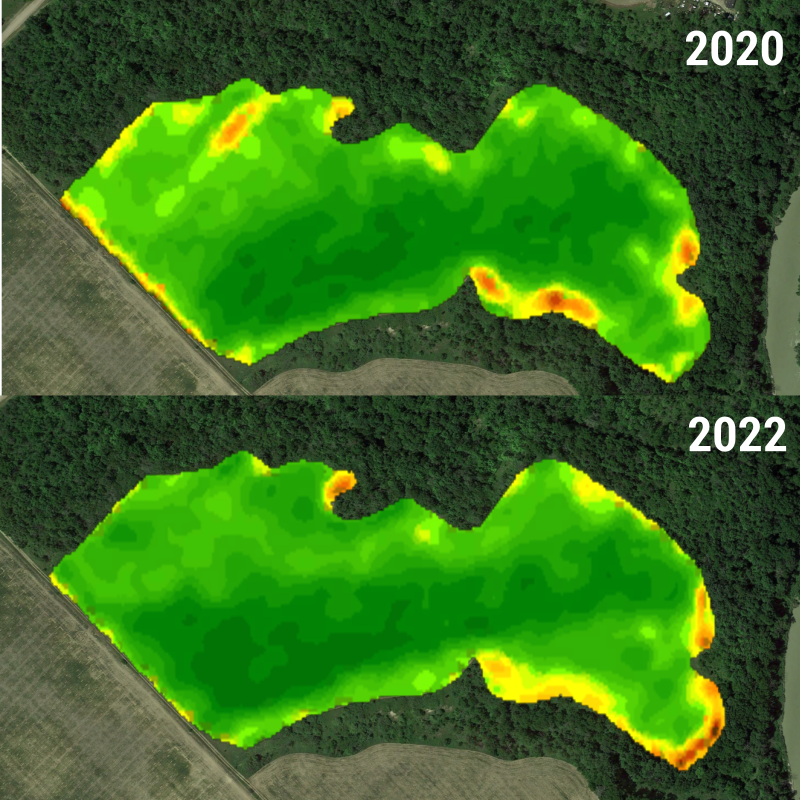
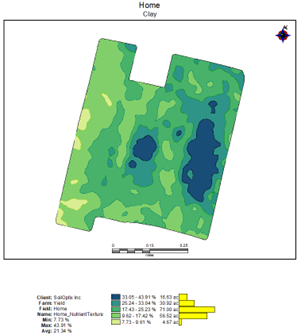
The results are in! After a successful 2024 harvest, we look at the yield data to evaluate the crop response after using SoilOptix®’s Plant Available Water layer to drive the VRT Seeding script.
Variable Rate Seeding Using Plant Available Water Layer Pt. 1
“What else can we do with this high-resolution soil information?” By: Steve Redmond; BSc As we progress through our Case Study series, you will notice that we have taken a purposeful journey through some of the basic uses of the SoilOptix® layers that allow an agronomist to amend a field for the “low hanging fruit”.… Read Full Article »
A Clear Advantage Over Zone Sampling
In years with low crop margins, high resolution provides an unquestionable return on investment with both higher yields from accurate fertilizer placement and either lower soil amendment rates or the optimization of existing budgets for soil amendments.
There’s no “Cookie-Cutter Approach” to Fertilization Strategies
Despite using standard crop production practices, challenges in the growing season can cause crops to suffer. In this Case Study, we examine how custom fertility strategies (outside of capturing the “low-hanging fruit”) can help maximize yields and increase productivity.
Return-on-Investment Through VRT Phosphorus and Potassium
One of the questions that always arises when new technology, especially Precision Ag offerings, is presented to cautious farmers can be summarized as “Okay, the maps are pretty, so what?”
In this study, we explore how VRT Phosphorus and Potassium based on high density soil information can produce a significant ROI to farmers.
SoilOptix® Custom Layers: What is Loam, Leakability & Plant Available Water?
In this report, we evaluate SoilOptix®’s custom data layers and how these can be applied efficiently to extend the possibilities of soil texture and physical property management practices.
VRT Magnesium and Potassium in Calcareous Soils in Ontario
Gamma radiation mapping and developing layers of individual soil nutrients has enabled VRT applications of potassium and magnesium that have helped to balance these important cations and improve the yield and quality of crops grown in these soils.
Prescription Zones for Variable Rate Applications
In precision agriculture, VRA is the practice of varying the amount of inputs (such as fertilizer, seed, or chemicals) applied to different parts of a field based on the unique characteristics of those areas. For a long time, VRA has been commonly utilized in row crops, but its use in the permanent crop industry has only recently emerged. This will allow orchard farmers to maximize yields while minimizing costs and environmental impact.
Technology Comparison Study
In this study completed by Dr. Viacheslav Adamchuk, in partnership with OMAFRA New Directions Program in 2015, a comparative report was completed that evaluated various methods of soil mapping, including Grid Sampling, Electrical Conductivity, and SoilOptix®. Click the link above to view the PDF report, and see the differences between the outputs of each technology… Read Full Article »
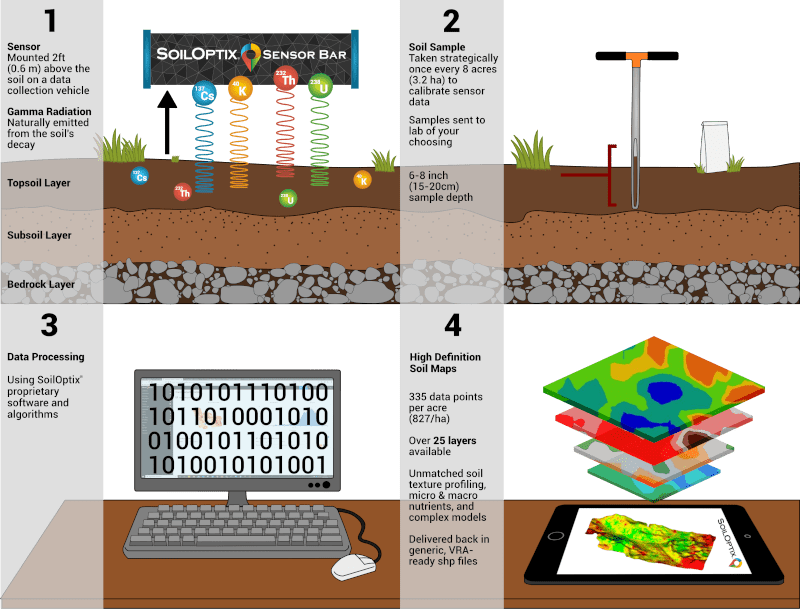
From Start to Finish: How SoilOptix® Technology Works
The SoilOptix® process from in field collection to a final data layer involves a standard four step process; from soil mapping, extraction of soil samples, data processing and finally retrieval of results.
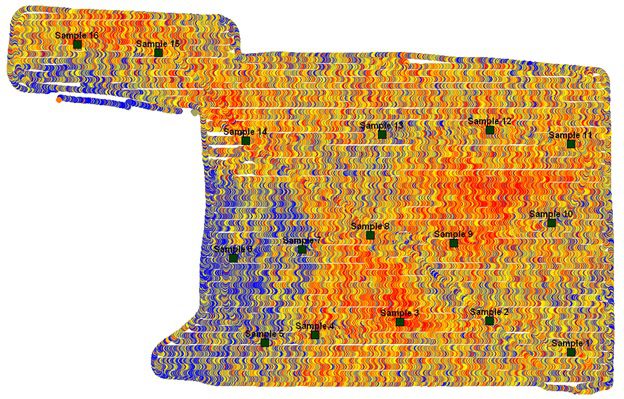
Soil Variation Based on Count Rate Map
It is known that there is soil texture variation across space and utilizing soil sensors like SoilOptix® gamma radiation detector can assist in mapping and understanding where these changes occur.